HashSet and TreeSet both implement same interface i.e java.util.Set interface and they posses the quality of Set interface means duplicate elements are not allowed. Both HashSet and TreeSet are used for to store unique elements, but HashSet doesn't care about any order and TreeSet keeps thing in order. Ordering or sorting on TreeSet can be customized by using Comparator interface, by default TreeSet uses elements natural order for sorting, which is defined by compareTo() method of java.lang.Comparable interface. What is difference between HashSet and TreeSet is is also one the frequently asked Java interview question, So you should know about similarities and difference between them. It also helps you to understand when to use both TreeSet and HashSet and whats are the scenario when we should use this sets. Let's go through the similarities and difference between HashSet and TreeSet in Java.
Read more »
Search
Thursday, July 30, 2015
Wednesday, July 29, 2015
OOP Concepts And Advanced Java Tutorials For WebDriver
Earlier we learnt many different basic java software development language's OOP concepts tutorials which are required to Initiate WebDriver software testing tool learning process and pass Interviews on Initial levels. Now let's try to understand advanced Java OOP concepts and some of the advanced java tutorials which will help you during WebDriver framework creation for your software web application. It will also help you to attend an Interview If you have 2+ years experience In WebDriver software testing tool.
First of all I recommend you to learn basic java tutorials from bellow given link.
First of all I recommend you to learn basic java tutorials from bellow given link.
VIEW BASIC JAVA TUTORIALS LINKS
Advanced Java OOP Concepts
- Encapsulation In Java
- Polymorphism In Java
- What Is An Abstract Class In Java?
- What Is Method Overloading In Java?
- Similarities And Difference Between Abstract Class And Interface
- Usage of "final" Keyword In Java
More tutorials are coming soon.
What Is Encapsulation In Java?
Many times when you will go to attend WebDriver Interview on 2+ years experience, Interviewer will ask you about Encapsulation. Best answer on Encapsulation In Java Is as bellow.
Encapsulation
Encapsulation In Java Is one of the OOP fundamental concept. It Is process of packing code and data together In to a single Unit. Best example Is capsule where powder of several medicines Is packed In single unit.
It Is also known as "data hiding" technique as fields of class are declared private and providing access to the fields via public methods. So anyone can not access private data fields directly outside the class. We can use setter and getter methods to get and set data In to It.
Advantages of Encapsulation
Few advantages of encapsulation.
- It Increase the usability.
- It promotes the easy maintenance.
- It makes the class easy to use for clients
- Data access and modification control
- It Is easy to change one part of code without affecting other part of code.
Example of Encapsulation
Let's look at very simple example of encapsulation In java. I have created encapsulation class Encaps.java as bellow.
Encaps.java
package oopbasics;
public class Encaps {
private String name;
private int rollNo;
//Data setter method
public void setName(String newName) {
name = newName;
}
//Data setter method
public void setrollNo(int newrollNo) {
rollNo = newrollNo;
}
//Data getter method
public String getName() {
return name;
}
//Data getter method
public int getrollNo() {
return rollNo;
}
}In above class, I have created data setter and getter public methods to set and get data. All variables are declared as private to no one can access and modify them directly from outside the class.
Now we can set and get values from Encaps.java class as bellow.
Encaps.java
package oopbasics;
public class exeEncaps {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Created object of Encaps class to set and get data.
Encaps encaps = new Encaps();
//Set data using setter methods of Encaps class.
encaps.setName("Monika");
encaps.setrollNo(56);
//Get data using getter methods of Encaps class.
System.out.println("RollNo : "+encaps.getrollNo()+", Name : "+encaps.getName());
}
}Output of above example Is as bellow.
RollNo : 56, Name : MonikaThis Is the best explanation of encapsulation. You can find more links to read basic java tutorials on THIS PAGE.
How to join two threads in Java? Thread.join() example
You can join two threads in Java by using join() method from java.lang.Thread class. Why do you join threads? because, you want one thread to wait for another before starts processing. It's like a relay race where second runner waits until first runner comes and hand over flag to him. Remember, unlike sleep(), join() is not a static method so you need an object of java.lang.Thread class to call this method. Now, who calls and who waits and which thread dies? for example, if you have two threads in your program main thread and T1 which you have created. Now if your main thread execute this line T1.join() (main thread execute whatever you have written in main method) then main thread will wait for T1 thread to finish its execution. Immediate effect of this call would be that main thread will stop processing immediately and will not start until T1 thread has finished. So, what will happen if T1 is not yet started and there is no one to start T1 thread? Well, then you have a deadlock but if its already finished then main thread will start again, provided it get the CPU back. In this tutorial, you will learn how to make three threads execute in a order by using join() method. You an also check out Java Threads By Scott Oaks and Henry Wong to get a good starting overview of several fundamentals of threads and multi-threading.
Read more »
Monday, July 27, 2015
OCAJP 7 or OCAJP 8? Which Java Certification should I take?
Java certification is great way to learn and master The Java programming language, do well on interview and get recognition in job, but most common reason of doing Java certification is to find a job. After Oracle's acquisition and dividing old SCJP exam into two exams OCAJP and OCPJP, it has become really confusing for many developers to decide which Java certification exam they should take. Since technologies change fast and Java is no exception, its just an year when Java 8 was released and now people are talking about Java 9. In general, it is better to go with the latest version of a certification, which is currently available i.e. the Java 8 version. But in case of Java certifications, it's not that simple. Many of my reader email me about my advice to decide between Java SE 6, 7 and 8 exams before zeroing one. After answering their emails, I realize its better to jolt down important points for everyone's benefit. Here are things you should consider before buying Java certification voucher and starting your preparation.
Read more »
Sunday, July 26, 2015
Latest Interview Questions On Selenium Advanced Usage
Part 23
108 : I wants to pass parameter In software test case through testng.xml file. How can I do It?
Answer : You can use <parameter> node under <test> node In testng.xml file with parameter name and value. Then you can use @Parameters annotation with parameter name In your test case of software web application. VIEW USAGE OF @PARAMETER ANNOTATION.
109 : My page contains file upload field but I am not able to upload file using selenium webdriver software testing tool. Is there any other way using which I can upload file In selenium test?
Answer : If you are not able to upload file using selenium webdriver then you can create file upload script In AutoIT and then you can use It In selenium webdriver software test. You can refer bellow given articles to learn more about It.
- What Is AutoIT V3
- Steps To Download And Install AutoIT V3
- Creating AutoIt Script To Upload File On Web Page
- Upload File In Selenium WebDriver Using AutoIt
110 : I wants to set size and position of my browser window. Do you know how to do it in selenium webdriver?
Answer : We can use setSize function to set size of window and setPosition function to set position of browser window. VIEW EXAMPLE.
111 : Is there any way to get size and position of browser window in selenium webdriver?
Answer : Yes.. We can get it using webdriver functions getSize and getPosition. VIEW MORE
112 : I wants to scroll my software web application page by 300 pixel. Tell me how can i do it?
Answer : We can use javascript executor with window.scrollBy(x,y) to scroll page in x or y directions. VIEW MORE DETAIL
Top 40 Java Web Services Interview Questions and Answers
Web services interview questions are mostly asked in Software development Positions. We have already shared the frequently asked core java interview questions and tricky java interview questions.
So below are the answers to the frequently asked web services interview questions.
Q1 What are web services ?
According to oracle docs, web services can be defined as
Main characteristics of the Web Services are :
1. Interoperability
2. Extensibility
3. Machine processable descriptions.
for example in simple words , when we call somebody so the person dialing and calling is the client application , while person receiving the call is server application and "hello" word is the protocol as similar to HTTP request .
Q2 What is the difference between SOA and a web service?
Web Services is a realization of SOA concept, that leverages XML, JSON, etc. and common Internet protocols such as HTTP(S), SMTP, etc.
Q4 What is REST?
Below are the main differences between REST and SOAP web service
Q8 What is JAX-WS?
Q9 What is JAXB?
Q10 Can we send soap messages with attachments?
Q12 What is XOP?
Q13 What is a SOAP envelope element?
SOAP namespace defines the Envelope as a SOAP Envelope.
Q15 What is the SOAP encoding?
Q16 What does SOAP encodingStyle attribute defines?
Q17 What are 2 styles web service’s endpoint by using JAX-WS?
Q18 What is encoding rules for header entries?
Q19 What is the wsimport tool?
Q20 What is the wsgen tool?
Q21 What is the difference between SOAP and other remote access techniques?
Q22 What is a resource in a REST?
Q23 What are HTTP methods supported by REST?
Q24 Whether can use GET request instead of POST to create a resource?
It is not possibly, because GET can’t change a resource.
Q25 What is the difference between PUT and POST?
Need to use PUT when can update a resource completely through a specific resource. For example, if know that an article resides at http://javahungry.blogspot.com/article/123, can PUT a new resource representation of this article through a PUT on this URL. If do not know the actual resource location for instance, when add a new article, can use POST.
Q26 What is WADL?
Q27 What are frameworks available to implement REST web services?
Q28 What is the Restlet framework?
Q29 What is the Jersey framework?
Jersey is open source framework for developing RESTful Web Services in Java that provides support for JAX-RS APIs and serves as a JAX-RS (JSR 311 & JSR 339) Reference Implementation. It has advantages such as
Q30 What is the RESTeasy framework?
RESTeasy is a JBoss project, which implements of the JAX-RS specification. It has benefits such as
Q31 What is the difference between AJAX and REST?
Q32 What tool are required to test REST services?
Q33 What does a @Path annotation do?
On calling URI: “/persons” result: getPerson is called
Q34 What does a @PathParam do?
On calling URI: “/persons/1” result: getPersonById is called, id : 1
Q35 What does a @QueryParam do?
On calling URI: “/persons/query?from=10&to=20&orderBy=age&orderBy=name” result: getPersons is called, from : 10, to : 20, orderBy[age, name]
Q36 What does a @MatrixParam do?
On calling URI: “/books/2015” result: getBooks is called, year : 2015, author : null, country : null
Q37 What does a @FormParam do?
HTML form:
Q39 How to get HTTP request header in JAX-RS (2 ways)?
On calling URI: “/persons/get” result: getPerson is called, personAgent : Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; rv:5.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/5.0
On calling URI: “/persons/get” result: getPerson is called, personAgent : Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; rv:5.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/5.0
Q40 How to download file in JAX-RS?
Please mention in the comments if you have any doubts regarding java web services interview questions and answers.
So below are the answers to the frequently asked web services interview questions.
Q1 What are web services ?
According to oracle docs, web services can be defined as
Web services are client and server applications that communicate over the World Wide Web’s (WWW) HyperText Transfer Protocol (HTTP). Web services provide a standard means of inter operating between software applications running on a variety of platforms and frameworks.
Main characteristics of the Web Services are :
1. Interoperability
2. Extensibility
3. Machine processable descriptions.
for example in simple words , when we call somebody so the person dialing and calling is the client application , while person receiving the call is server application and "hello" word is the protocol as similar to HTTP request .
Q2 What is the difference between SOA and a web service?
SOA (Service-Oriented Architecture) is an architectural pattern that makes possible for
services to interact with one another independently.
Web Services is a realization of SOA concept, that leverages XML, JSON, etc. and common Internet protocols such as HTTP(S), SMTP, etc.
SOA is a system-level architectural style that tries to expose business. WOA is an interface-level architectural style that focuses on the means by which these service capabilities are exposed to consumers.
Q3 What is SOAP?
SOAP (Simple Object Access Protocol) is a transport protocol for sending and receiving requests and responses on XML format, which can be used on top of transport protocols such as HTTP, SMTP, UDP, etc.
Q3 What is SOAP?
SOAP (Simple Object Access Protocol) is a transport protocol for sending and receiving requests and responses on XML format, which can be used on top of transport protocols such as HTTP, SMTP, UDP, etc.
Q4 What is REST?
REST (REpresentational State Transfer) is an architectural style by which data can be transmitted over transport protocol such as HTTP(S).
Q5 What is the difference between a REST web service and a SOAP web service?
Q5 What is the difference between a REST web service and a SOAP web service?
Below are the main differences between REST and SOAP web service
- REST supports different formats like text, JSON and XML; SOAP only supports XML;
- REST works only over HTTP(S) on a transport layer; SOAP can be used different protocols on a transport layer;
- REST works with resources, each unique URL is some representation of a resource; SOAP works with operations, which implement some business logic through different interfaces;
- SOAP based reads can’t be cached, for SOAP need to provide caching; REST based reads can be cached;
- SOAP supports SSL security and WS-security(Web Service-security); REST only supports SSL security;
- SOAP supports ACID (Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, Durability); REST supports transactions, but it is neither ACID compliant nor can provide two phase commit.
Q6 How to decide which one of web service to use REST or SOAP?
“REST vs SOAP” we can rephrased to "Simplicity vs Standard". Of course, "Simplicity" with REST at most cases wins, it wins in performance, scalability and support for multiple data formats, but SOAP is favored where service requires comprehensive support for security (WS-security) and transactional safety (ACID).
“REST vs SOAP” we can rephrased to "Simplicity vs Standard". Of course, "Simplicity" with REST at most cases wins, it wins in performance, scalability and support for multiple data formats, but SOAP is favored where service requires comprehensive support for security (WS-security) and transactional safety (ACID).
“SOAP”
Q7 What is WSDL?
Q7 What is WSDL?
WSDL (Web Services Description Language) is an XML format for describing web services and how to access them.
JAX-WS (Java API for XML Web Services) is a set of APIs for creating web services in XML format.
JAXB (Java Architecture for XML Binding) is a Java standard that defines how Java objects are converted from and to XML. It makes reading and writing of XML via Java relatively easy.
Yes, we can send different formats such as PDF document, image or other binary file with soap messages as an attachment. Messages send using the binary data. SOAP messages is attached with MIME extensions that come in multipart/related.
An example:
MIME-Version: 1.0
Content-Type: Multipart/Related; boundary=MIME_boundary; type=text/xml;
start="<claim061400a.xml@ javahungry.com>"
Content-Description: This is the optional message description.
<?xml version='1.0' ?>
<SOAP-ENV:Envelope
xmlns:SOAP-ENV="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/envelope/">
<SOAP-ENV:Body>
..
<theSignedForm href="cid:claim061400a.tiff@javahungry.com"/>
..
</SOAP-ENV:Body>
</SOAP-ENV:Envelope>
--MIME_boundary
Content-Type: image/tiff
Content-Transfer-Encoding: binary
Content-ID: <claim061400a.tiff@javahungry.com>
...binary TIFF image...
--MIME_boundary—
Q11 What is MTOM?
Q11 What is MTOM?
MTOM (Message Transmission Optimization Mechanism) is a mechanism for transmitting large binary attachments with SOAP messages as raw bytes, allowing for smaller messages.
XOP (XML-binary Optimized Packaging) is a mechanism defined for the serialization of XML Information Sets that contain binary data, as well as deserialization back into the XML Information Set.
SOAP envelop element is the root element of a SOAP message which defines the XML document as a SOAP message.
An example:
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<soap:Envelope
xmlns:soap="http://www.w3.org/2001/12/soap-envelope"
soap:encodingStyle="http://www.w3.org/2001/12/soap-encoding">
...
Message information
...
</soap:Envelope>
Q14 What does a SOAP namespace defines?
<soap:Envelope
xmlns:soap="http://www.w3.org/2001/12/soap-envelope"
soap:encodingStyle="http://www.w3.org/2001/12/soap-encoding">
...
Message information
...
</soap:Envelope>
Q14 What does a SOAP namespace defines?
SOAP namespace defines the Envelope as a SOAP Envelope.
An example:
xmlns:soap=http://www.w3.org/2001/12/soap-envelope
SOAP encoding is a method for structuring the request which is suggested within the SOAP specification, known as the SOAP serialization.
SOAP encodingStyle defines the serialization rules used in a SOAP message. This attribute may appear on any element, and is scoped to that element's contents and all child elements not themselves containing such an attribute. There is no default encoding defined for a SOAP message.
An example:
SOAP-ENV:encodingStyle="http://www.w3.org/2001/12/soap-encoding"
- RPC (remote procedure call) style web service in JAX-WS;
- document style web service in JAX-WS.
- a header entry is identified by its fully qualified element name, which consists of the namespace URI and the local name. All immediate child elements of the SOAP Header element must be namespace-qualified.
- the SOAP encodingStyle attribute may be used to indicate the encoding style used for the header entries.
- the SOAP mustUnderstand attribute and SOAP actor attribute may be used to indicate how to process the entry and by whom.
The wsimport tool is used to parse an existing Web Services Description Language (WSDL) file and generate required files (JAX-WS portable artifacts) for web service client to access the published web services: https://docs.oracle.com/javase/6/docs/technotes/tools/share/wsimport.html
The wsgen tool is used to parse an existing web service implementation class and generates required files (JAX-WS portable artifacts) for web service deployment: http://docs.oracle.com/javase/6/docs/technotes/tools/share/wsgen.html
- What the tool are required to test SOAP services?
SOAPUI tool for SOAP WS: http://www.soapui.org/
Q21 What is the difference between SOAP and other remote access techniques?
- SOAP is simple to use and it is non - symmetrical unlike DCOM or CORBA is highly popular and usually have complexity in them.
- SOAP provides greater platform independent with the language independence unlike DCOM or CORBA doesn't provide any of these.
- SOAP uses HTTP as its transport protocol and the data are being saved in XML format that can be ready by human, whereas DCOM or CORBA have their own binary formats that are used to transport the data in complicated manner.
SOAP identify the object other than URL endpoint. SOAP objects are stateless and it is hard to maintain that. Whereas, it is not hard to maintain in case of other remote access techniques.
“REST”
Q22 What is a resource in a REST?
A resource is a unique URL with representation of an object which we can get contents via GET and modify via PUT, POST, DELETE.
- GET;
- POST;
- PUT;
- DELETE;
- OPTIONS;
- HEAD.
It is not possibly, because GET can’t change a resource.
Need to use PUT when can update a resource completely through a specific resource. For example, if know that an article resides at http://javahungry.blogspot.com/article/123, can PUT a new resource representation of this article through a PUT on this URL. If do not know the actual resource location for instance, when add a new article, can use POST.
PUT is idempotent, while POST is not. It means if use PUT an object twice, it has no effect.
WADL (Web Application Description Language) is a XML description of a deployed RESTful web application.
Jersey, Restlet, EasyRest, etc.
Restlet is a lightweight, comprehensive, open source RESTful web API framework for the Java platform.
It has advantages such as
- websocket and server-sent events support;
- HTTP/2 support;
- transparent HTTP PATCH support;
- client cache service;
- fluent APIs.
http://restlet.com/
Jersey is open source framework for developing RESTful Web Services in Java that provides support for JAX-RS APIs and serves as a JAX-RS (JSR 311 & JSR 339) Reference Implementation. It has advantages such as
- contains support for Web Application Description Language (WADL);
- contains Jersey Test Framework which lets run and test Jersey REST services inside JUnit;
- supports for the REST MVC pattern, which would allow to return a View from Jersey services rather than just data.
https://jersey.java.net/
RESTeasy is a JBoss project, which implements of the JAX-RS specification. It has benefits such as
- fully certified JAX-RS implementation; supports HTTP 1.1 caching semantics including cache revalidation;
- JAXB marshalling into XML, JSON, Jackson, Fastinfoset, and Atom as well as wrappers for maps, arrays, lists, and sets of JAXB Objects;
- OAuth2 and Distributed SSO with JBoss AS7;
- rich set of providers for: XML, JSON, YAML, Fastinfoset, Multipart, XOP, Atom, etc.
http://resteasy.jboss.org/
- in Ajax, the request are sent to the server by using XMLHttpRequest objects; REST have a URL structure and a request/response pattern the revolve around the use of resources;
- Ajax eliminates the interaction between the customer and server asynchronously; REST requires the interaction between the customer and server;
- Ajax is a set of technology; REST is a type of software architecture and a method for users to request data or information from servers.
Firefox “poster” plugin for RESTFUL services. https://addons.mozilla.org/en-us/firefox/addon/poster/
@Path annotation binds URI pattern to a Java method.
import javax.ws.rs.GET;
import javax.ws.rs.Path;
import javax.ws.rs.core.Response;
@Path("/persons")
public class PersonRestService {
@GET
public Response getPerson() {
return Response.status(200).entity("getPerson is called").build();
}
@GET
@Path("/vip")
public Response getPersonVIP() {
return Response.status(200).entity("getPersonVIP is called").build();
}
}
On calling URI: “/persons” result: getPerson is called
On calling URI: “/persons/vip” result: getPersonVIP is called
@PathParam annotation injects the value of URI parameter that defined in @Path expression.
import javax.ws.rs.GET;
import javax.ws.rs.Path;
import javax.ws.rs.PathParam;
import javax.ws.rs.core.Response;
@Path("/persons")
public class PersonRestService {
@GET
@Path("{id}")
public Response getPersonById(@PathParam("id") String id) {
return Response.status(200).entity("getPersonById is called, id : " + id).build();
}
}
On calling URI: “/persons/1” result: getPersonById is called, id : 1
@QueryParam annotation injects URI query parameter into Java method.
import java.util.List;
import javax.ws.rs.GET;
import javax.ws.rs.Path;
import javax.ws.rs.QueryParam;
import javax.ws.rs.core.Response;
@Path("/persons")
public class PersonService {
@GET
@Path("/query")
public Response getPersons(
@QueryParam("from") int from,
@QueryParam("to") int to,
@QueryParam("orderBy") List<String> orderBy) {
return Response
.status(200)
.entity("getPersons is called, from : " + from + ", to : " + to
+ ", orderBy" + orderBy.toString()).build();
}
}
On calling URI: “/persons/query?from=10&to=20&orderBy=age&orderBy=name” result: getPersons is called, from : 10, to : 20, orderBy[age, name]
@MatrixParam are a set of “name=value” in URI path.
import javax.ws.rs.GET;
import javax.ws.rs.MatrixParam;
import javax.ws.rs.Path;
import javax.ws.rs.PathParam;
import javax.ws.rs.core.Response;
@Path("/books")
public class BookService {
@GET
@Path("{year}")
public Response getBooks(@PathParam("year") String year,
@MatrixParam("author") String author,
@MatrixParam("country") String country) {
return Response
.status(200)
.entity("getBooks is called, year : " + year
+ ", author : " + author + ", country : " + country)
.build();
}
}
On calling URI: “/books/2015” result: getBooks is called, year : 2015, author : null, country : null
On calling URI: “/books/2015;author= doyle;country=scotland” result: getBooks is called, year : 2015, author : doyle, country : scotland
@FormParam bind HTML form parameters value to a Java method.
import javax.ws.rs.FormParam;
import javax.ws.rs.POST;
import javax.ws.rs.Path;
import javax.ws.rs.core.Response;
@Path("/persons")
public class PersonService {
@POST
@Path("/add")
public Response addPerson(
@FormParam("name") String name,
@FormParam("age") int age) {
return Response.status(200)
.entity("addPerson is called, name : " + name + ", age : " + age)
.build();
}
}
HTML form:
<html>
<body>
<form action="/persons/add" method="post">
<p>
Name : <input type="text" name="name" />
</p>
<p>
Age : <input type="text" name="age" />
</p>
<input type="submit" value="Add Person" />
</form>
</body>
</html>
- inject directly with @HeaderParam;
import javax.ws.rs.GET;@Path("/persons") public class PersonService { @GET@Path("/get") public Response getPerson( @HeaderParam("person-agent") String personAgent) { return Response.status(200) .entity("getPerson is called, personAgent : " + personAgent) .build(); } }
import javax.ws.rs.Path;
import javax.ws.rs.HeaderParam;
import javax.ws.rs.core.Response;
On calling URI: “/persons/get” result: getPerson is called, personAgent : Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; rv:5.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/5.0
- pragmatically via @Context.
import javax.ws.rs.GET;
import javax.ws.rs.Path;
import javax.ws.rs.core.Context;
import javax.ws.rs.core.HttpHeaders;
import javax.ws.rs.core.Response;
@Path("/persons")
public class PersonService {
@GET
@Path("/get")
public Response getPerson(@Context HttpHeaders headers) {
String personAgent = headers.getRequestHeader("person-agent").get(0);
return Response.status(200)
.entity("getPerson is called, personAgent : " + personAgent)
.build();
}
}
On calling URI: “/persons/get” result: getPerson is called, personAgent : Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; rv:5.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/5.0
- put @Produces(“?”) on service method, with a Response return type. Instead “?” write a type text/plain, image/png, etc.
- set “Content-Disposition” in Response header to tell browser pop up a download box for user to download.
import java.io.File;
import javax.ws.rs.GET;
import javax.ws.rs.Path;
import javax.ws.rs.Produces;
import javax.ws.rs.core.Response;
import javax.ws.rs.core.Response.ResponseBuilder;
@Path("/image")
public class ImageService {
private static final String FILE_PATH = "c:\\my.png";
@GET
@Path("/get")
@Produces("image/png")
public Response getFile() {
File file = new File(FILE_PATH);
ResponseBuilder response = Response.ok((Object) file);
response.header("Content-Disposition",
"attachment; filename=image_from_server.png");
return response.build();
}
}
Please mention in the comments if you have any doubts regarding java web services interview questions and answers.
Friday, July 24, 2015
22 Array Concepts Interview Questions Answers in Java
Array is one of the fundamental data structure and most of other data structures are based upon it e.g. List, Hash tables are based upon arrays. Array based questions are quite popular on Java interviews. There are two types of question you will find, first which are based upon array implementation in Java and second which are based upon how to use array data structure to solve some problems. First type of question is quite popular in telephonic round of Java interview and second is usually asked on written test and face-to-face interviews. These questions are mostly collected from Java interviews for junior and intermediate programmers, who has 0 to 5 years of working experience in Java. Some tricky questions like question no 2 and 15 are also good for senior and more experienced Java professionals. In fact, one of my friend didn't got the question 15 right, he was actually surprised by the fact that you can make an array volatile in Java. Anyway, if you are seriously preparing for Java interview then you have to do more than just preparing for array based questions. I suggest you to take a look at Cracking the Coding Interview book, which contains 150 Programming Questions and Solutions, good enough to clear any Java interview. If you want to prepare more Java specific questions then you can also take a look at Java Programming Interview Exposed, which contains lots of questions from Java and related technology e.g. Maven, JUnit, Servlet, JSP, Android and others.
Read more »
Thursday, July 23, 2015
How to calculate Maximum and minimum in Java? Beginner Tutorial
Today's programming exercise for beginner is to write a Java program to take input from user and find out maximum and minimum number and print them into console. Purpose of this article is to teach you how to get input from user in Java and how to use java.lang.Math class to perform some mathematical operation e.g. max, min or average. You can use Scanner class, added in Java 1.5 to read user input from console. Scanner needs an InputStream to read data and because you are reading from console, you can pass System.in, which is InputStream for Eclipse console, or command prompt, depending upon what you are using. This class also helps you to convert user input into require data type e.g. if user enter numbers then you must convert then into int data type and store them into int variable as shown in our example. You can use nextInt() method to read user input as Integer. Similarly you can use nextLine() to read user input as String. There are other methods available to read float, double, or boolean from command prompt. Once you got both the numbers, it just matter of using relational operator less than and greater than to find smaller and larger number, as shown in following example. After that you can Math.max() to find maximum of two numbers, it should be same as your earlier result. Similarly, we will ask User to enter number again and will display minimum of two. I also suggest you to read Head First Java 2nd Edition book, if you have just started learning Java. It is one of the best book to learn Java in quick time.
Read more »
Wednesday, July 22, 2015
Steps To Get Element XPath/CSS Using Firebug And FirePath Add-On Of Firefox
We learnt how to Install firebug and firepath add-on In Mozilla Firefox browser In my previous post. Now this Is time to learn how to get XPath and CSS Path of any element using firebug and firepath add-on. If you remember, We already learnt different ways to get XPath of any element
using many different examples In THIS POST. So I will not describe same thing here. We will look only at how to use firebug and firepath add-on to get XPath and CSS Path In this post.There are two types of XPath. 1. Relative XPath 2. Absolute XPath. You can read difference between Relative and Absolute XPath on THIS PAGE.
We will use "First name" text box which Is given on THIS PAGE to get Its the XPath and CSS Path.
Get Relative XPath of Element using firebug and firepath
Steps to get relative XPath
Go to THIS PAGE.
- Click on Firebug Icon from toolbar as shown In bellow Image. It will open firebug Inspector window.
- Select FirePath tab from firebug window.
- Click on firebug Inspector Icon.
- Click on "First name" text box.
- You will get relative XPath of "First name" text box In XPath text box.
Get Absolute XPath of Element using firebug and firepath
Only difference between steps to get relative XPath and absolute XPath Is you need to select "Generate absolute XPath" option from FirePath tab option selector as bellow.
Steps to get absolute XPath.
Go to THIS PAGE.
- Click on Firebug Icon from toolbar.
- Select FirePath tab.
- Select "Generate absolute XPath" option from FirePath tab option selector.
- Follow steps 3 to 5 of get relative XPath section. You will get absolute XPath of element as shown In bellow Image.
Get CSS Path of Element using firebug and firepath
Now you know steps to get XPath of element using firebug and firepath. You need to select CSS to get CSS path of any element as described In bellow Image.
Steps to get CSS path of element.
- Select CSS as shown In bellow Image.
- Follow steps 3 to 5 of get relative XPath section. You will CSS path of element as shown In bellow Image.
This way we can use firebug and firepath add on to get XPath or CSS path of any element. Also you can view THIS POST to know how to use firebug and firepath with webdriver firefox instance.
Monday, July 20, 2015
Why String is final or immutable in Java with Example
Before going into details as why String is final or immutable in java , first let us understand the meaning of the term "immutable".
What does immutable means?
What does immutable means?
According to our good buddy, “thefreedictionary”, immutable means “not capable or susceptible to change”.
Note : In java , if an object is immutable then it can not be changed after creation.
The String Class
The String class represents a set of characters enclosed in a pair of double quotes (“”). All String literals in Java, such as "hello", are implemented as instances of the String class.
Strings are immutable; their values cannot be changed after they have been created, while StringBuffers and StringBuilders supports mutable versions of the String object.
For example:
String str = "hello";
is equivalent to:
char ch[] = {'h', 'e', 'l', ‘l’, ‘o’};
String str = new String(ch);
There are several ways on how to create a String object, by checking the Java API documentation; you’ll see that the String class has about 15 constructors including the 2 deprecated ones. Deprecated constructors and methods are encouraged not to be used in the current Java version.
Here are the two common ways on how to create a String object.
String str1 = new String(“hello”);
String str2 = “java”;
The first one uses the keyword new followed by the String constructor; while the second one uses a direct assignment.
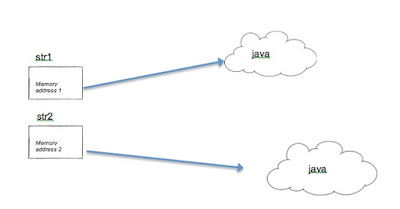
- Is there a difference between the two? Let’s take a look at the two code snippets; this will also explain why String objects are immutable.
Sample Code Snippet #1:
String str1 = new String("java");
String str2 = new String("java");
System.out.println(str1 == str2);
System.out.println(str1.equals(str2));
Snippet Output #1:
false
true
That’s why when str1 and str2 was compared using the double equals operator (==), the output was false because they were comparing the addresses of both variables. The .equals method on the other hand compares if both str1 and str2 have identical String objects that they are referring to.
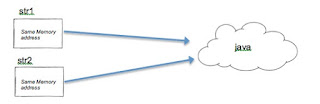
Sample Code Snippet #2:
String str1 = “java”;
String str2 = “java;
System.out.println(str1 == str2);
System.out.println(str1.equals(str2));
Snippet Output #2:
true
true
Snippet #2 created only 1 object but had two variables holding them. That is why str1 and str2 has the same address. Therefore when they are compared using the double equals operator (==) they returned true. A second String object was not forcibly created because the constructor was not explicitly called. The statement str2 = “java” only assigns the already existing String object in the memory to the String variable str2.
During concatenation, we can also see that the String object also shows their immutability by creating a new object after concatenation. Concatenation can be done by calling the concat method or by using the concatenation symbol (+).
Sample Code Snippet #3:
String str = “hello ”;
System.out.println(str);
is the same as:
String str = “hello ”;
str.concat(“world”);
System.out.println(str);
Both sample codes will printout hello world as the output.
Here’s the explanation:
String str = “hello ”;
str.concat(“world”);
After concatenating the Strings “hello ” and “world”, it will produce a new object “hello world” which is a new object that has a new address.
3. Why Strings are immutable.
Security is one of the reasons that I can think of why String objects are immutable. Strings are usually used as parameters in several Java methods that can be used to access data sources like databases, files or even objects that can be found across the network. Once you call a method that takes an immutable object like Strings, you can be sure that the data that is passed won’t change. It simply cannot change.
Imagine the threat and security problems that you may have if you are accessing a method via RMI (Remote Method Invocation) and the method that you are calling requires you to pass a String object. Before reaching the requested method, there is no assurance that the String objects that you sent is the same String object that is received on the other VM (Virtual Machine). This can result to a serious security problem.
4. What do I use if I need a mutable version of a String object?
Incase you are in need of mutable String objects, you may use StringBuffer or StringBuilder. Both are found inside the java.lang package and both classes contains the same set of methods that can change the object like append, insert, reverse and a lot more. Both of these classes can also take in a String object as a parameter on their respective constructors.
Here’s how to create StringBuffer and StringBuilder objects that accepts a String parameter.
StringBuffer sBuffer = new StringBuffer(“this is a string”);
StringBuilder sBuilder = new StringBuilder(“this is another string”);
The difference between StringBuffer and a StringBuilder object is the thread safety capability.
StringBuffer can not be used by multiple concurrent users because it is thread-safe. But StringBuilder is not thread-safe; therefore it can only be used by multiple threads.
Thread-safety also has its minor trade off. Thread-safe objects like StringBuffer objects may require a slightly larger memory space during runtime compared with StringBuilder objects. This is because during runtime, the thread activation and passivation process can happen at runtime if the thread-pool ran out of threads. This is the reason why most of the mobile devices like PDA’s, mobile phones and terminal card readers only uses StringBuilder and not StringBuffer. Aside from having a smaller memory requirement, StringBuilder are also used by a single process only.
Read Also : How to Reverse a String in Java with Example
5. The String class is a final class.
According to the Java API Documentation the String class declaration is:
public final class String extends Object
implements Serializable, Comparable<String>, CharSequence
Declaring a class as final means that the class cannot be extended by another class. You cannot create a subclass from a final class.
Here’s a non-working Code Snippet:
public class MyStringVersion extends String
{}
This snippet won’t compile because the class MyStringVersion is extending the class String.
This simply shows that the String class cannot be extended or inherited. This is good.
Imagine, if Strings are not final, you can create a subclass and instantiate two objects from different classes that can look alike and be seen as Strings but are actually different. This can cause several problems in so many levels. Thats it for now just mention in comments if you have any other questions related to why string is immutable or final in java.
How to stop a thread in Java? Example
Today we're going to learn about how to stop a thread in Java. It's easy to start a thread in Java because you have a start() method but it's difficult to stop the thread because there is no working stop() method. Well, there was a stop() method in Thread class, when Java was first released but that was deprecated later. In today's Java version, You can stop a thread by using a boolean volatile variable. If you remember, threads in Java start execution from run() method and stop, when it comes out of run() method, either normally or due to any exception. You can leverage this property to stop the thread. All you need to do is, create a boolean variable e.g. bExit or bStop. Your thread should check its value every iteration and comes out of loop and subsequently from run() method if bExit is true. In order to stop the thread, you need to set value of this boolean variable to true when you want to stop a running thread. Since you are setting this variable from a different thread e.g. main thread, its important to mark this variable volatile, otherwise its possible for the running thread to cache its value and never check back to main memory for updated value and running infinitely. When you make a variable volatile, running thread will not cache its value in its local stack and always refer main memory. Volatile variable also provides happens before guarantee, which can be used to synchronize values. If you want to understand multi-threading and concurrency in right way, I strongly suggest to read Java Concurrency in Practice twice. Its one of the most accurate, thorough and practical book in Java multi-threading.
Read more »
Sunday, July 19, 2015
How to search an element inside LinkedList in Java? Example
You can search an element inside LinkedList in Java by using indexOf() and lastIndexOf() methods. Though LinkedList doesn't support random search like ArrayList, you can still go through the list, check each element and find out whether its interested element or not. Since java.util.LinkedList is an implementation of doubly linked list, these two methods are quite handy to search from either ends e.g. indexOf() method start search from head and return an elements position, while lastIndexOf() starts search from tail. Though, position is not relative to ends, they are always calculated from head. You can also use these two methods to find out duplicate elements. If an element is appeared twice in linked list then indexOf() and lastIndexOf() method will return different positions for that because it will be found at different position from head and tail. For unique elements, both these methods will return same position. In this article, you will see examples of both indexOf() and lastIndexOf() methods to search a given element inside LinkedList. As I said before, since LinkedList doesn't support random search and searching an element require list traversal, which means time complexity will be O(n). BTW, if you are good in Java but lacks data structure and algorithm skill, I strongly suggest to read Data Structures and Algorithm Analysis in Java by Mark A. Wiess. It's a great book to build your foundation on data structure and algorithm using Java programming language.
Read more »
How To Attach Firebug and FirePath Add-On To Firefox Driver Instance
Firebug and FirePath add-ons of Firefox browser are playing major role to get the XPath and CSS path of any element easily and quickly. Earlier we learnt how to use firebug and firepath add-on with Firefox browser to get XPath or CSS of any element In THIS POST. Now supposing I need both
these add-ons In Firefox Driver Instance when I run my test using selenium WebDriver FirefoxDriver Instance. Is It possible? Yes - Let's see how can we do It.As you know, It Is launching Firefox browser Instance with fresh profile every time when you execute selenium WebDriver test. So Firebug and FirePath will be not available In that fresh created profile of WebDriver FirefoxDriver Instance. Bellow given steps will add Firebug and FirePath In WebDriver FirefoxDriver Instance for you.
Download .xpi files of Firebug and FirePath add-on
First of all we need to download .xpi files of Firebug and FirePath add-on and then we will attach both these files with WebDriver FirefoxDriver Instance profile during test execution.
Download latest .xpi file of Firebug
You need Google Chrome or Internet Explorer browser to download .xpi file.
- Open Google Chrome browser.
- In Google Chrome browser, Go to Firebug add-on DOWNLOAD PAGE.
- Click on "Download Now" button on Firebug add-on download page as shown In bellow Image.
- Click on "download anyway" link as shown bellow. It will download .xpi file of firebug.
Download latest .xpi file of Firebug
- Open Chrome browser.
- In Chrome browser, Go to Firepath add-on DOWNLOAD PAGE.
- Click on "Download Now" button and then click on "download anyway" link. firepath's .xpi file will be downloaded.
Current latest version of firebug Is 2.0.10 and firepath Is 0.9.7.1.1 so downloaded file will be "firebug-2.0.10-fx.xpi" and "firepath-0.9.7.1-fx.xpi". Firebug and FirePath versions can be change In future so file name will be different In future based on version.
Put firebug and firepath .xpi files In D: drive.
Create and run WebDriver test with firebug and firepath add-on
Now we can launch FirefoxDriver Instance with firebug and firepath add-on. We will create custom FirefoxDriver profile on run time and then attach both these add-ons with that custom profile. So new launched FirefoxDriver Instance will have firebug and firepath add-ons.
Execute bellow given test In your eclipse and verify firefox driver Instance Is launched with firebug and firepath add-ons or not.
package Testing_Pack;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import org.openqa.selenium.WebDriver;
import org.openqa.selenium.firefox.FirefoxDriver;
import org.openqa.selenium.firefox.FirefoxProfile;
public class Firebug {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// Set Firebug and Firepath xpi file's path.
// Note : both file's name and path should be proper. Please verify It twice.
File firebug_path = new File("D:\\firebug-2.0.10-fx.xpi");
File firepath_path = new File("D:\\firepath-0.9.7.1-fx.xpi");
// Create firefox driver Instance profile.
FirefoxProfile firefoxprofile = new FirefoxProfile();
// Add Firebug add-on to new created profile of Firefox browser.
firefoxprofile.addExtension(firebug_path);
// Add FirePath add-on to new created profile of Firefox browser.
firefoxprofile.addExtension(firepath_path);
// Pass new created Firefox profile to the FirefoxDriver instance.
WebDriver driver = new FirefoxDriver(firefoxprofile);
driver.get("http://only-testing-blog.blogspot.in/2014/04/calc.html");
}
}When I run above test, my firefox driver Instance Is launched with firebug and firepath add-ons as shown In bellow Image.
This way you can use firebug and fire path add-on run time to get XPath of any element when you run your tests. THIS POST will show you how to get xpath or CSS path using firebug and firepath.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)